Decoding of motor imagery applied to EEG data decomposed using CSP. Here the classifier is applied to features extracted on CSP filtered signals.
See http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Common_spatial_pattern and [1]. The EEGBCI dataset is documented in [2]. The data set is available at PhysioNet [3].
| [1] | Zoltan J. Koles. The quantitative extraction and topographic mapping of the abnormal components in the clinical EEG. Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology, 79(6):440–447, December 1991. |
| [2] | Schalk, G., McFarland, D.J., Hinterberger, T., Birbaumer, N., Wolpaw, J.R. (2004) BCI2000: A General-Purpose Brain-Computer Interface (BCI) System. IEEE TBME 51(6):1034-1043. |
| [3] | Goldberger AL, Amaral LAN, Glass L, Hausdorff JM, Ivanov PCh, Mark RG, Mietus JE, Moody GB, Peng C-K, Stanley HE. (2000) PhysioBank, PhysioToolkit, and PhysioNet: Components of a New Research Resource for Complex Physiologic Signals. Circulation 101(23):e215-e220. |
# Authors: Martin Billinger <martin.billinger@tugraz.at>
#
# License: BSD (3-clause)
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mne import Epochs, pick_types, find_events
from mne.channels import read_layout
from mne.io import concatenate_raws, read_raw_edf
from mne.datasets import eegbci
from mne.decoding import CSP
print(__doc__)
# #############################################################################
# # Set parameters and read data
# avoid classification of evoked responses by using epochs that start 1s after
# cue onset.
tmin, tmax = -1., 4.
event_id = dict(hands=2, feet=3)
subject = 1
runs = [6, 10, 14] # motor imagery: hands vs feet
raw_fnames = eegbci.load_data(subject, runs)
raw_files = [read_raw_edf(f, preload=True) for f in raw_fnames]
raw = concatenate_raws(raw_files)
# strip channel names of "." characters
raw.rename_channels(lambda x: x.strip('.'))
# Apply band-pass filter
raw.filter(7., 30.)
events = find_events(raw, shortest_event=0, stim_channel='STI 014')
picks = pick_types(raw.info, meg=False, eeg=True, stim=False, eog=False,
exclude='bads')
# Read epochs (train will be done only between 1 and 2s)
# Testing will be done with a running classifier
epochs = Epochs(raw, events, event_id, tmin, tmax, proj=True, picks=picks,
baseline=None, preload=True)
epochs_train = epochs.copy().crop(tmin=1., tmax=2.)
labels = epochs.events[:, -1] - 2
Out:
Extracting edf Parameters from /home/ubuntu/mne_data/MNE-eegbci-data/physiobank/database/eegmmidb/S001/S001R06.edf...
Setting channel info structure...
Creating Raw.info structure...
Reading 0 ... 19999 = 0.000 ... 124.994 secs...
Ready.
Extracting edf Parameters from /home/ubuntu/mne_data/MNE-eegbci-data/physiobank/database/eegmmidb/S001/S001R10.edf...
Setting channel info structure...
Creating Raw.info structure...
Reading 0 ... 19999 = 0.000 ... 124.994 secs...
Ready.
Extracting edf Parameters from /home/ubuntu/mne_data/MNE-eegbci-data/physiobank/database/eegmmidb/S001/S001R14.edf...
Setting channel info structure...
Creating Raw.info structure...
Reading 0 ... 19999 = 0.000 ... 124.994 secs...
Ready.
Setting up band-pass filter from 7 - 30 Hz
l_trans_bandwidth chosen to be 2.0 Hz
h_trans_bandwidth chosen to be 7.5 Hz
Filter length of 528 samples (3.300 sec) selected
Removing orphaned offset at the beginning of the file.
89 events found
Events id: [1 2 3]
45 matching events found
0 projection items activated
Loading data for 45 events and 801 original time points ...
0 bad epochs dropped
Classification with linear discrimant analysis
from sklearn.lda import LDA # noqa
from sklearn.cross_validation import ShuffleSplit # noqa
# Assemble a classifier
lda = LDA()
csp = CSP(n_components=4, reg=None, log=True)
# Define a monte-carlo cross-validation generator (reduce variance):
cv = ShuffleSplit(len(labels), 10, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
scores = []
epochs_data = epochs.get_data()
epochs_data_train = epochs_train.get_data()
# Use scikit-learn Pipeline with cross_val_score function
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline # noqa
from sklearn.cross_validation import cross_val_score # noqa
clf = Pipeline([('CSP', csp), ('LDA', lda)])
scores = cross_val_score(clf, epochs_data_train, labels, cv=cv, n_jobs=1)
# Printing the results
class_balance = np.mean(labels == labels[0])
class_balance = max(class_balance, 1. - class_balance)
print("Classification accuracy: %f / Chance level: %f" % (np.mean(scores),
class_balance))
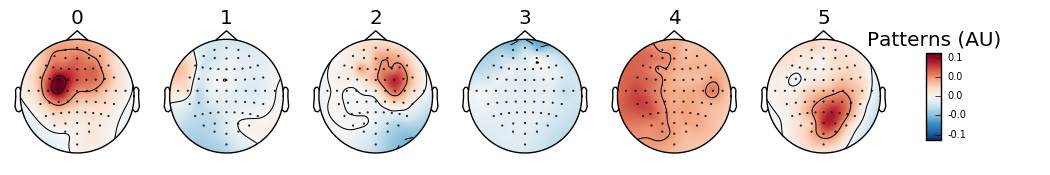
# plot CSP patterns estimated on full data for visualization
csp.fit_transform(epochs_data, labels)
evoked = epochs.average()
evoked.data = csp.patterns_.T
evoked.times = np.arange(evoked.data.shape[0])
layout = read_layout('EEG1005')
evoked.plot_topomap(times=[0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5], ch_type='eeg', layout=layout,
scale_time=1, time_format='%i', scale=1,
unit='Patterns (AU)', size=1.5)
Out:
Classification accuracy: 0.944444 / Chance level: 0.533333
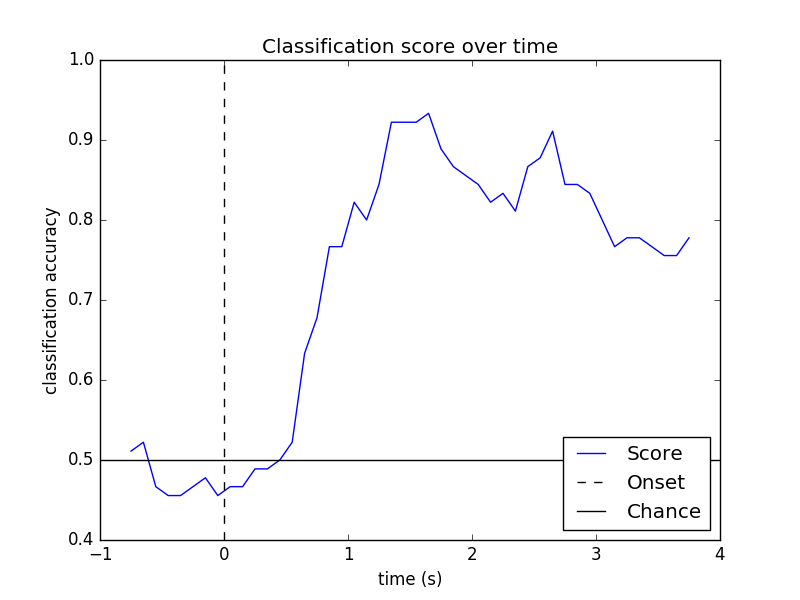
Look at performance over time
sfreq = raw.info['sfreq']
w_length = int(sfreq * 0.5) # running classifier: window length
w_step = int(sfreq * 0.1) # running classifier: window step size
w_start = np.arange(0, epochs_data.shape[2] - w_length, w_step)
scores_windows = []
for train_idx, test_idx in cv:
y_train, y_test = labels[train_idx], labels[test_idx]
X_train = csp.fit_transform(epochs_data_train[train_idx], y_train)
X_test = csp.transform(epochs_data_train[test_idx])
# fit classifier
lda.fit(X_train, y_train)
# running classifier: test classifier on sliding window
score_this_window = []
for n in w_start:
X_test = csp.transform(epochs_data[test_idx][:, :, n:(n + w_length)])
score_this_window.append(lda.score(X_test, y_test))
scores_windows.append(score_this_window)
# Plot scores over time
w_times = (w_start + w_length / 2.) / sfreq + epochs.tmin
plt.figure()
plt.plot(w_times, np.mean(scores_windows, 0), label='Score')
plt.axvline(0, linestyle='--', color='k', label='Onset')
plt.axhline(0.5, linestyle='-', color='k', label='Chance')
plt.xlabel('time (s)')
plt.ylabel('classification accuracy')
plt.title('Classification score over time')
plt.legend(loc='lower right')
plt.show()
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 3.244 seconds)