ERP decoding with Xdawn. For each event type, a set of spatial Xdawn filters are trained and applied on the signal. Channels are concatenated and rescaled to create features vectors that will be fed into a Logistic Regression.
| [1] | Rivet, B., Souloumiac, A., Attina, V., & Gibert, G. (2009). xDAWN algorithm to enhance evoked potentials: application to brain-computer interface. Biomedical Engineering, IEEE Transactions on, 56(8), 2035-2043. |
| [2] | Rivet, B., Cecotti, H., Souloumiac, A., Maby, E., & Mattout, J. (2011, August). Theoretical analysis of xDAWN algorithm: application to an efficient sensor selection in a P300 BCI. In Signal Processing Conference, 2011 19th European (pp. 1382-1386). IEEE. |
# Authors: Alexandre Barachant <alexandre.barachant@gmail.com>
#
# License: BSD (3-clause)
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.cross_validation import StratifiedKFold
from sklearn.pipeline import make_pipeline
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report, confusion_matrix
from sklearn.preprocessing import MinMaxScaler
from mne import io, pick_types, read_events, Epochs
from mne.datasets import sample
from mne.preprocessing import Xdawn
from mne.decoding import Vectorizer
from mne.viz import tight_layout
print(__doc__)
data_path = sample.data_path()
Set parameters and read data
raw_fname = data_path + '/MEG/sample/sample_audvis_filt-0-40_raw.fif'
event_fname = data_path + '/MEG/sample/sample_audvis_filt-0-40_raw-eve.fif'
tmin, tmax = -0.1, 0.3
event_id = dict(aud_l=1, aud_r=2, vis_l=3, vis_r=4)
# Setup for reading the raw data
raw = io.read_raw_fif(raw_fname, preload=True)
raw.filter(1, 20)
events = read_events(event_fname)
picks = pick_types(raw.info, meg=False, eeg=True, stim=False, eog=False,
exclude='bads')
epochs = Epochs(raw, events, event_id, tmin, tmax, proj=False,
picks=picks, baseline=None, preload=True,
verbose=False)
# Create classification pipeline
clf = make_pipeline(Xdawn(n_components=3),
Vectorizer(),
MinMaxScaler(),
LogisticRegression(penalty='l1'))
# Get the labels
labels = epochs.events[:, -1]
# Cross validator
cv = StratifiedKFold(y=labels, n_folds=10, shuffle=True, random_state=42)
# Do cross-validation
preds = np.empty(len(labels))
for train, test in cv:
clf.fit(epochs[train], labels[train])
preds[test] = clf.predict(epochs[test])
# Classification report
target_names = ['aud_l', 'aud_r', 'vis_l', 'vis_r']
report = classification_report(labels, preds, target_names=target_names)
print(report)
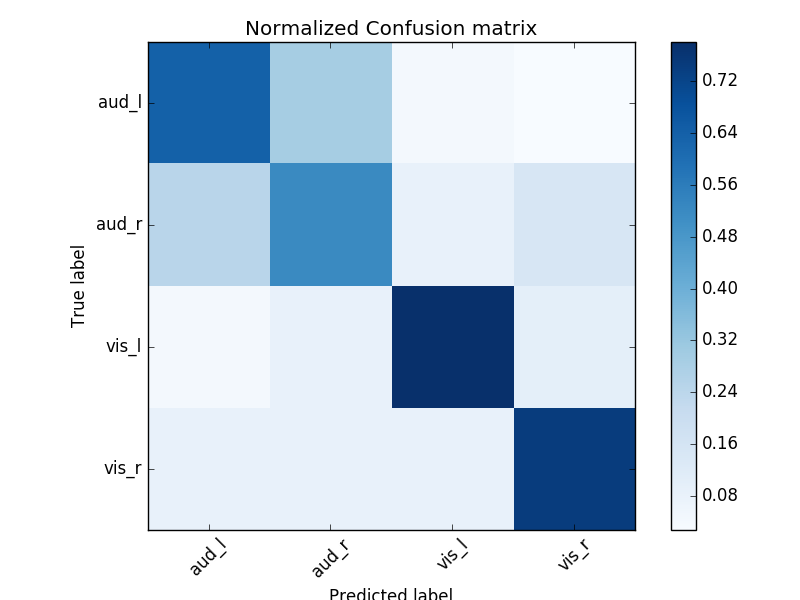
# Normalized confusion matrix
cm = confusion_matrix(labels, preds)
cm_normalized = cm.astype(float) / cm.sum(axis=1)[:, np.newaxis]
# Plot confusion matrix
plt.imshow(cm_normalized, interpolation='nearest', cmap=plt.cm.Blues)
plt.title('Normalized Confusion matrix')
plt.colorbar()
tick_marks = np.arange(len(target_names))
plt.xticks(tick_marks, target_names, rotation=45)
plt.yticks(tick_marks, target_names)
tight_layout()
plt.ylabel('True label')
plt.xlabel('Predicted label')
plt.show()
Out:
Opening raw data file /home/ubuntu/mne_data/MNE-sample-data/MEG/sample/sample_audvis_filt-0-40_raw.fif...
Read a total of 4 projection items:
PCA-v1 (1 x 102) idle
PCA-v2 (1 x 102) idle
PCA-v3 (1 x 102) idle
Average EEG reference (1 x 60) idle
Range : 6450 ... 48149 = 42.956 ... 320.665 secs
Ready.
Current compensation grade : 0
Reading 0 ... 41699 = 0.000 ... 277.709 secs...
Setting up band-pass filter from 1 - 20 Hz
l_trans_bandwidth chosen to be 1.0 Hz
h_trans_bandwidth chosen to be 5.0 Hz
Filter length of 991 samples (6.600 sec) selected
precision recall f1-score support
aud_l 0.63 0.64 0.63 72
aud_r 0.54 0.52 0.53 73
vis_l 0.79 0.78 0.79 73
vis_r 0.72 0.74 0.73 70
avg / total 0.67 0.67 0.67 288
Total running time of the script: ( 0 minutes 4.408 seconds)